Load balancing Inspirata Dynamyx

Useful resources
About Inspirata Dynamyx
Dynamyx from Inspirata affords an ‘open’ architecture purposely designed to enable healthcare providers to arrive at their preferred blend of laboratory and diagnostic technologies. In providing a vendor-agnostic, end-to-end digital pathology solution deliberately architected for multi-vendor environments, Inspirata assist high-throughput clinical laboratories navigate the specific and frequent challenges of system interoperability while also allowing for increased resource flexibility and a future-proofing of investments culminating in an overall lower total cost of ownership.
Key benefits of load balancing
Here are a few key benefits of load balancing:
- Resilience
- High availability
- Scalability
How to load balance Inspirata Dynamyx
When load balancing Inspirata Dynamyx, we recommend that Layer 7 SNAT mode is used. This mode offers high performance with no real server or network changes required since replies go via the same path as the ingress traffic.
Using a layer 7 configuration will lose client source IP address transparency. If source IP transparency is required, i.e. if the back end servers must see inbound traffic as originating from the client’s true source address, then it is suggested to use either a layer 4 DR or NAT mode configuration. Ultimately, the final choice does depend on your specific requirements and infrastructure.
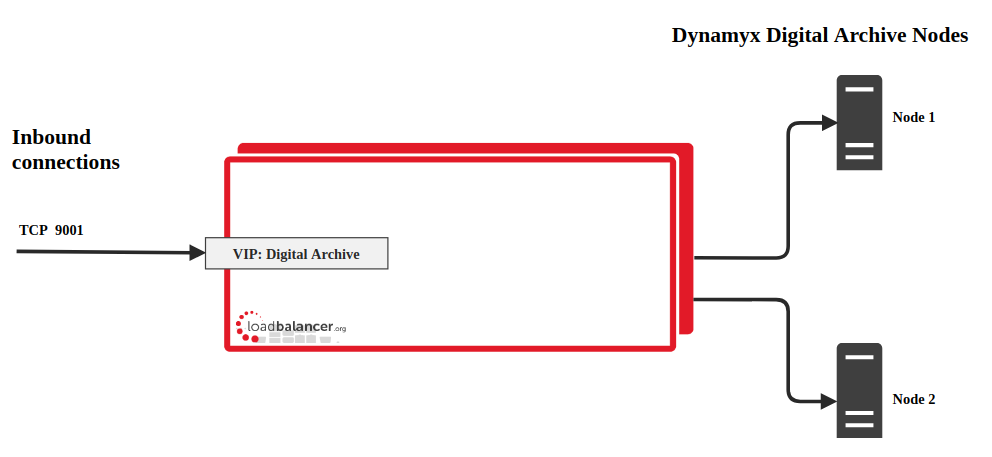
We recommend that load balancer appliances are deployed in pairs for high availability. A single unit is deployed first, adding a secondary slave unit – this is covered on page 17 of our deployment guide, below.
deployment guide

Inspirata Dynamyx Deployment Guide
Read deployment guidemanual

Administration manual v8
Read manualblogs

Four overlooked risks in NHS IT systems
Read blog
Digital pathology: five ways to ensure fast and successful adoption
Read blogwhite papers

The fast track to healthy digital pathology
Read white paper
The IT foundation for value-based healthcare
Read white paper
Fast healthcare interoperability resources (FHIR)
Read white paper

