Load balancing DataCore Swarm Gateway

Useful resources
About DataCore Swarm Gateway
DataCore Swarm Gateway provides an on-premise object storage solution allowing S3/HTTP access to any application, device, or end-user.
These services are presented via gateway servers. These gateways need to be load balanced in order to provide highly available and resilient service access.
Key benefits of load balancing
Here are a few key benefits:
- Ensures the application is always available
- Provides stable, optimal performance
- Ability to isolate servers which reduces risk when performing upgrades/maintenance
- Scalability
How to load balance DataCore Swarm Gateway
The load balancer can be deployed in 4 fundamental ways:
- Layer 4 DR mode
- Layer 4 NAT mode
- Layer 4 SNAT mode
- Layer 7 SNAT mode.
For DataCore Swarm Gateway, using Layer 4 DR mode is recommended. It offers the greatest raw performance and is particularly well suited to read-intensive storage scenarios.
Layer 7 SNAT mode is the simplest and most flexible solution. It must be used if the gateway servers are on a different network segment to the load balancers (no Layer 2 connectivity between them) or when it is not possible to make administrative changes to the gateway servers for some reason.
Layer 4 DR mode
One-arm direct routing (DR) mode is a very high performance solution that requires little change to your existing infrastructure.
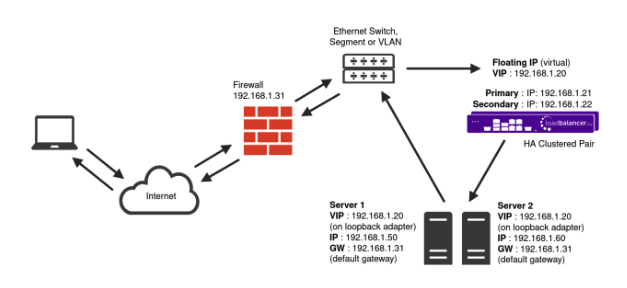
DR mode works by changing the destination MAC address of the incoming packet to match the selected Real Server on the fly which is very fast.
When the packet reaches the Real Server it expects the Real Server to own the Virtual Services IP address (VIP). This means that you need to ensure that the Real Server (and the load balanced application) respond to both the Real Server’s own IP address and the VIP.
The Real Servers should not respond to ARP requests for the VIP. Only the load balancer should do this. Configuring the Real Servers in this way is referred to as Solving the ARP problem.
On average, DR mode is 8 times quicker than NAT for HTTP, 50 times quicker for Terminal Services and much, much faster for streaming media or FTP.
The load balancer must have an Interface in the same subnet as the Real Servers to ensure Layer 2 connectivity required for DR mode to work.
The VIP can be brought up on the same subnet as the Real Servers, or on a different subnet provided that the load balancer has an interface in that subnet.
Port translation is not possible with DR mode, e.g. VIP:80 → RIP:8080 is not supported. DR mode is transparent, i.e. the Real Server will see the source IP address of the client.
Layer 7 SNAT Mode
Layer 7 SNAT mode uses a proxy (HAProxy) at the application layer. Inbound requests are terminated on the load balancer and HAProxy generates a new corresponding request to the chosen Real Server. As a result, Layer 7 is typically not as fast as the Layer 4 methods.
Layer 7 is typically chosen when enhanced options such as SSL termination, cookie based persistence, URL rewriting, header insertion/deletion etc. are required, or when the network topology prohibits the use of the Layer 4 methods.

Because Layer 7 SNAT mode is a full proxy, any server in the cluster can be on any accessible subnet, including across the Internet or WAN.
Layer 7 SNAT mode is not transparent by default i.e. the Real Servers will not see the source IP address of the client, they will see the load balancer’s own IP address by default, or any other local appliance IP address if preferred (e.g. the VIP address). This can be configured per Layer 7 VIP.
If required, the load balancer can be configured to provide the actual client IP address to the Real Servers in two ways:
- Either by inserting a header that contains the client’s source IP address, or
- By modifying the Source Address field of the IP packets and replacing the IP address of the load balancer with the IP address of the client.
Layer 7 SNAT mode can be deployed using either a one-arm or two-arm configuration. For two-arm deployments, eth0 is normally used for the internal network and eth1 is used for the external network, although this is not mandatory.
No mode-specific configuration changes to the load balanced Real Servers are required.
Port translation is possible with Layer 7 SNAT mode e.g. VIP:80 → RIP:8080 is supported. You should not use the same RIP:PORT combination for Layer 7 SNAT mode VIPs and Layer 4 SNAT mode VIPs because the required firewall rules conflict.
deployment guide

DataCore Swarm Gateway Deployment Brief
Read deployment guidemanual

Administration manual
Read manualcase studies

A world-renowned research laboratory safeguards critical data with Loadbalancer.org and Dell EMC
Read case study
Cloudian HyperStore safeguards research data and intellectual assets for a leading UK research university
Read case studyblogs

How to load balance and optimize Hitachi Content Platform (HCP)
Read blog
How load balancing helps to store and protect petabytes of data
Read blogother

Load balancing object storage for increased availability, performance, scalability and resilience
Read other

