Load balancing Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS/RDP)

Useful resources
About Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS/RDP)
Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS) is an industry leading desktop virtualization platform. It is the successor to Microsoft Terminal Services and facilitates the efficient, flexible and secure deployment of a Windows desktop environment and/or Windows applications, to users both locally and remotely.
Key benefits of load balancing
Here are a few key benefits:
- Ensures the application is always available
- Provides a stable, optimal performance
- Ability to isolate servers which reduces risk when performing upgrades/maintenance
- Scalability
Microsoft’s Enterprise solutions are at the heart of businesses everywhere. Loadbalancer.org is officially certified for all of Microsoft’s key applications which you can find here. More details on the Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS/RDP) components, how it works, and prerequisites for load balancing can be found in our deployment guide, available to view below.
How to load balance Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS/RDP)
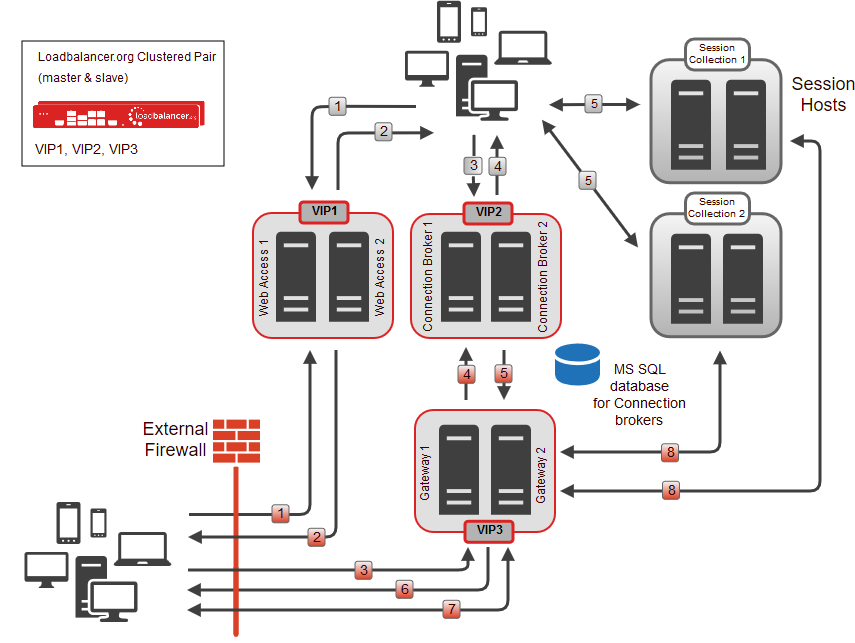
The load balancer is typically used to load balance multiple Connection Brokers, multiple Web Access Servers and multiple Gateway Servers. Session Hosts are normally load balanced by the Connection Brokers, although the load balancer can also be used as detailed in the deployment guide referenced below.
Remote Desktop Services (RDS) protocol table
| Protocol | Ports | Role | Load balancing methods |
| TCP/HTTPS | 443 | HTTPS (RD Gateway & RD Web Access) | Layer 7 |
| TCP | 3389 | RDP | Layer 7 |
| UDP | 3389 | RDP (UDP support was added in RDP v8.0) | Layer 4 |
| UDP | 3391 | RDP for RD Gateway | Layer 4 |
deployment guide

Microsoft Remote Desktop Services (RDS) Deployment Guide
Read deployment guidemanual

Administration manual v8
Read manualcase study

Fluid Networks - Load balancing Microsoft Remote Desktop Services
Read case studyblogs

Microsoft drops support for mstshash cookies
Read blog
Open Source Windows service for reporting server load back to HAProxy
Read blog
Load balancing Windows Terminal Server - HAProxy and RDP Cookies or Microsoft Connection Broker
Read blogother

Overview of Remote Desk Services (2008 R2)
Read other
Overview of Remote Desktop Services (2012)
Read other

