Load balancing Verint WorkForce Optimization
Benefits of load balancing Verint WorkForce Optimization
Load balancing Verint WorkForce Optimization (WFO) provides three main benefits:
- High Availability (HA): A load balancer continuously monitors the health of the application servers. If a server becomes unresponsive (fails a “health check”), the load balancer immediately stops sending new traffic to it, redirecting all requests to the remaining healthy servers. This prevents a single point of failure from causing an outage. This feature is crucial for WFO components like real-time adherence monitoring, scheduling, and recording, ensuring that managers and agents can access critical tools without interruption, which is vital for continuous contact center operations.
- Enhanced scalability: Verint WFO often experiences traffic spikes during activities like massive report generation, large-scale schedule publishing, or high-volume call/screen recording. Load balancing allows the system to scale horizontally by adding more servers to the pool to handle sudden increases in demand without degrading response times for users. This improvement ensures a more stable and consistent user experience, which is particularly important for WFO, where managers rely on real-time data and agents use the system for time-sensitive tasks like checking adherence or requesting shift swaps. A fast, reliable system increases employee engagement and operational efficiency.
- Improved performance: Load balancing distributes incoming user requests (e.g., for reports, schedules, recordings) and workload processing evenly across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming a bottleneck. It ensures that all available server resources are efficiently used. Instead of one server handling 100% of the load while others are idle, the load balancer might split the load across four servers, with each handling 25%. By efficiently distributing the workload and preventing server overload, a load balancer significantly reduces the time it takes for the Verint WFO application to process requests. Requests are directed to the least busy or fastest-responding server (depending on the balancing algorithm), resulting in faster page loads, quicker report generation, and more responsive user interfaces for managers and agents.
About Verint WorkForce Optimization
Verint WorkForce Optimization (WFO) is a unified suite of cloud solutions for capturing interactions and managing the performance of employees across the enterprise.
This includes workforce management, call recording, automated quality management, performance management, speech, text, and desktop analytics and much more.
Why Loadbalancer.org for Verint WorkForce Optimization?
Loadbalancer’s intuitive Enterprise Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is designed to save time and money with a clever, not complex, WebUI.
Easily configure, deploy, manage, and maintain our Enterprise load balancer, reducing complexity and the risk of human error. For a difference you can see in just minutes.
And with WAF and GSLB included straight out-of-the-box, there’s no hidden costs, so the prices you see on our website are fully transparent.
More on what’s possible with Loadbalancer.org.
How to load balance Verint WorkForce Optimization
The load balancer can be deployed in 4 fundamental ways: Layer 4 DR mode, Layer 4 NAT mode, Layer 4 SNAT mode, and Layer 7 Reverse Proxy (Layer 7 SNAT mode).
For Verint WFO, Layer 4 SNAT mode is recommended.
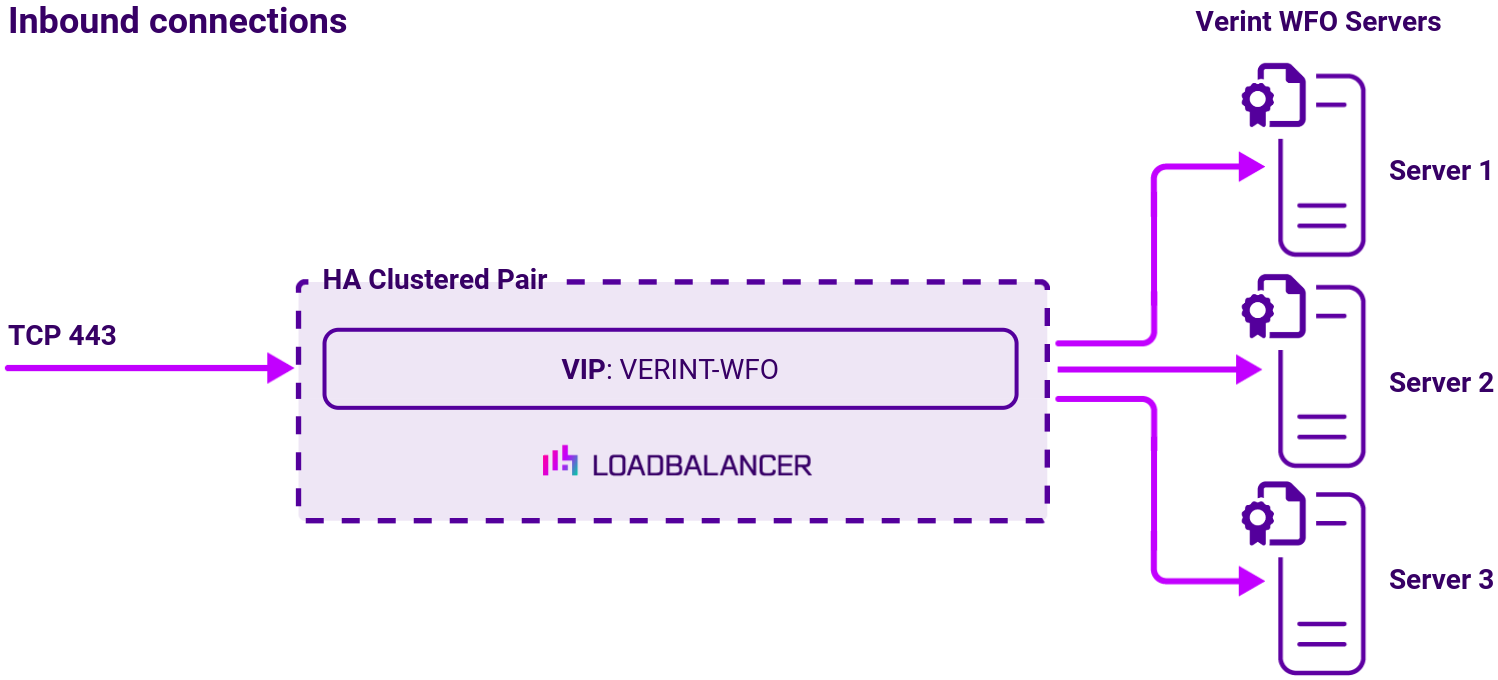
Virtual service (VIP) requirements
To provide load balancing and HA for Verint WFO, the following VIP is required:
| Ref. | VIP Name | Mode | Port(s) | Persistence Mode | Health Check |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIP 1 | VERINT-WFO | Layer 4 SNAT | 443 | Source IP | HTTPS (GET) |
Load balancing deployment concept
Note
The load balancer can be deployed as a single unit, although Loadbalancer.org recommends a clustered pair for resilience and high availability.
About Layer 4 SNAT mode
Layer 4 SNAT mode is a high performance solution, although not as fast as Layer 4 NAT mode or Layer 4 DR mode.
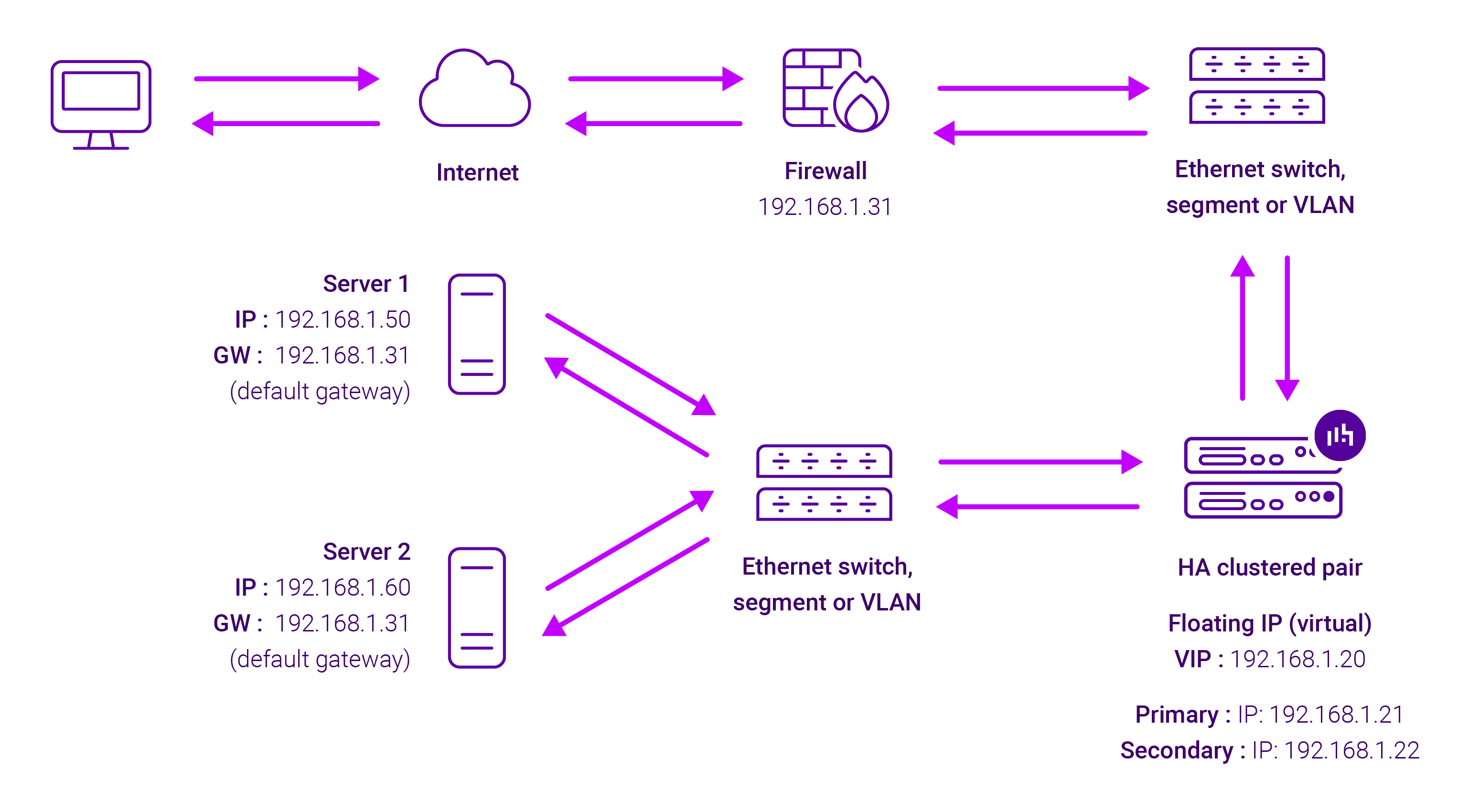
Real Servers in the cluster can be on any accessible network including across the Internet or WAN.
Layer 4 SNAT mode is not transparent, an iptables SNAT rule translates the source IP address to be the load balancer rather than the original client IP address.
Layer 4 SNAT mode can be deployed using either a one-arm or two-arm configuration. For two-arm deployments, eth1 is typically used for client side connections and eth0 is used for Real Server connections, although this is not mandatory since any interface can be used for any purpose.
This mode requires no mode-specific configuration changes to the load balanced Real Servers. Port translation is possible with Layer 4 SNAT mode, e.g. VIP:80 → RIP:8080 is supported. You should not use the same RIP:PORT combination for Layer 4 SNAT mode VIPs and Layer 7 Reverse Proxy mode VIPs because the required firewall rules conflict.