Load balancing Omnissa Horizon (formerly VMware Horizon)
Benefits of load balancing Omnissa Horizon
Load balancing Omnissa Horizon provides the following key benefits:
- High Availability (HA): This is arguably the most crucial benefit. By distributing client connections across multiple Connection Server or UAG instances, the failure of one server does not take the entire service offline. A load balancer constantly monitors the “health” of each server. If a server fails its health check, the load balancer instantly stops sending new user traffic to it, ensuring users are always directed to a working component. IT administrators can take a server offline (quiesce it) for patching, upgrades, or maintenance without impacting active user sessions or preventing new users from logging in, significantly improving operational flexibility.
- Scalability and performance: Load balancing allows you to easily scale your environment and ensures a consistent user experience. It intelligently distributes incoming user connection requests (for authentication and session brokering) across all available servers. This prevents any single server from becoming overloaded, which is essential for maintaining fast log-in times and preventing slow performance. As your organization grows or user demand spikes, you can simply add more Connection Servers or UAG appliances to the load-balanced pool to handle the increased load. The load balancer automatically incorporates them, allowing the environment to scale horizontally without complex reconfiguration.
- Simplified access and user experience: Load balancing provides a streamlined and consistent front-end for users. Instead of having users connect to a specific server’s name (e.g., server01.company.com), the load balancer presents a single, easy-to-remember Virtual IP (VIP) address or fully qualified domain name (FQDN) (e.g., vdi.company.com). Users only need to know this one public address, whether they are connecting internally or externally (via UAGs). The load balancer handles the complexity of routing the traffic to the correct backend server. For Horizon’s multi-protocol connections, the load balancer uses features like Source IP Affinity to ensure that all subsequent connection requests from a single user are directed back to the same Connection Server or UAG instance that initially authenticated them, which is vital for a smooth and uninterrupted user session.
About Omnissa Horizon
Omnissa Horizon (formerly known as VMware Horizon) is a commercial desktop and application virtualization product. It was developed by VMware and is now a core product of Omnissa, a company that was formed from the End-User Computing division of VMware after its acquisition by Broadcom.
It allows businesses to deliver virtual desktops and applications to users from a central location, whether on-premises or in the cloud. This means that instead of running software and an operating system directly on a user’s computer, those resources are hosted in a data center and streamed to the user’s device.
While the application name has changed, the product itself is a continuation of the Horizon 8 line. Any version of Horizon 8 that was released after the rebrand is now officially known as Omnissa Horizon.
Why Loadbalancer.org for Omnissa Horizon?
Loadbalancer’s intuitive Enterprise Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is designed to save time and money with a clever, not complex, WebUI.
Easily configure, deploy, manage, and maintain our Enterprise load balancer, reducing complexity and the risk of human error. For a difference you can see in just minutes.
And with WAF and GSLB included straight out-of-the-box, there’s no hidden costs, so the prices you see on our website are fully transparent.
More on what’s possible with Loadbalancer.org.
How to load balance Omnissa Horizon
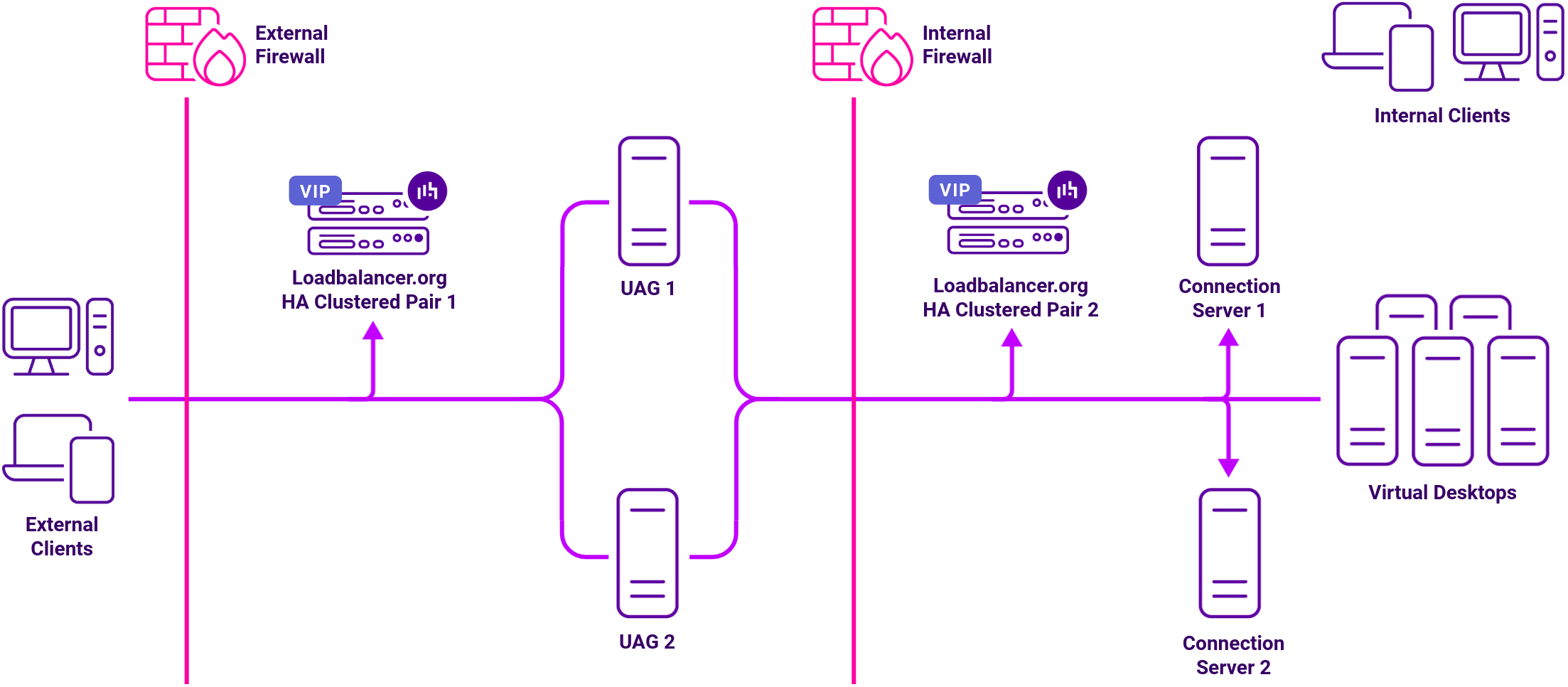
Connection Servers broker client connections, authenticate users, and direct incoming requests to the correct endpoint. Although the Connection Server helps form the connection, it typically does not act as part of the data path after the connection is established.
Security Servers are installed in the DMZ and add an additional layer of security between the Internet and the internal network for external users. Each Security Server must be paired with a Connection Server and forwards all traffic to that instance. This pairing requires the Connection Server to be in tunnel mode, which means it is not suitable for internal client connections, so two sets of Connection Servers are needed – one to handle connections from the paired Security Servers, the other to handle internal clients.
Access Point is a hardened SUSE Linux based appliance introduced in v6.2 as an alternatively to Security Server. Access Point was renamed Unified Access Gateway (UAG) in Horizon v7.0. UAG is now the preferred option over Security Server. Access Point / UAG is not paired, so only one set of Connection Servers is needed for both external and internal clients.
For high availability and scalability, VMware recommends that multiple Connection Servers and multiple Unified Access Gateways are deployed in a load-balanced cluster.
The load balancers can be configured in various ways to support internal and external clients as detailed in the deployment guides referenced below.
VMware Horizon Protocol Table
| Protocol | Port | Use |
|---|---|---|
| TCP | 443 | Various HTTPS traffic |
| TCP/UDP | 443 | Blast |
| TCP/UDP | 4172 | PColP |
| TCP/UDP | 8443 | Blast |
Load balancing deployment concept