Load balancing Meditech RESTful API
Benefits of load balancing Meditech RESTful API
The main benefits of load balancing Meditech RESTful API include:
- Enhanced performance and reduced latency: By distributing incoming API requests across a cluster of multiple Meditech RESTful API servers, a load balancer prevents any single server from becoming overwhelmed. Spreading the workload ensures that servers can process requests more efficiently, leading to significantly improved API response times—a critical factor for clinicians and integrated systems accessing patient data in real-time. The load balancer intelligently routes traffic to the healthiest or least-busy server, optimizing the use of all available resources and preventing performance degradation during high-traffic periods.
- High Availability (HA) and fault tolerance: In a healthcare setting, downtime for systems accessing the Electronic Health Record (EHR) can be life-threatening. Load balancing provides crucial redundancy. If one API server crashes, fails a health check, or needs maintenance, the load balancer automatically and instantly redirects all traffic to the remaining healthy servers. This failover process is often seamless to the user or integrated application, ensuring continuous, uninterrupted access to critical health data and promoting high system uptime.
- Scalability and capacity expansion: Load balancing makes it easy for an organization to grow its API capacity as patient load, integration needs, or data volume increases. When throughput limits are reached, you can simply add more stateless Meditech RESTful API servers to the pool. The load balancer automatically incorporates these new servers and begins distributing the load to them. This enables on-demand scalability without requiring a massive overhaul of the system, ensuring the infrastructure can keep pace with evolving interoperability requirements and increasing utilization.
About Meditech RESTful API
Meditech is a leading global provider of Electronic Healthcare Records (EHR) and interoperability solutions. The RESTful API Infrastructure allows MEDITECH and third party vendor software to securely access the MEDITECH EHR through APIs. Interoperability Services (or IOPS) — which is a component of the RESTful API Infrastructure and installed on the same machine(s) — adds a set of APIs to meet Meaningful Use Stage 3 (MU3) and Imaging Appropriate Use Criteria (AUC) requirements.
Note: RESTful API is independent from any other web products or interoperability interfaces MEDITECH offers and requires dedicated hardware.
Why Loadbalancer.org for Meditech RESTful API?
Loadbalancer’s intuitive Enterprise Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is designed to save time and money with a clever, not complex, WebUI.
Easily configure, deploy, manage, and maintain our Enterprise load balancer, reducing complexity and the risk of human error. For a difference you can see in just minutes.
And with WAF and GSLB included straight out-of-the-box, there’s no hidden costs, so the prices you see on our website are fully transparent.
More on what’s possible with Loadbalancer.org.
How to load balance Meditech
An optimal RESTful API Infrastructure configuration consists of two or more servers running the RESTful API services as well as Interoperability Services. The cluster helps to ensure better performance and failover protection for the Infrastructure. These servers host the web services which clients connect to.
Meditech recommend either SSL termination or SSL bridging when using a load balancer. SSL passthrough where SSL is terminated on the backend API servers is not recommended.
Meditech also recommend that one VIP is used for all API environments and a separate VIP is used for all Application environments.
Load balancing deployment concept
Meditech RESTful API can be load balanced in two different ways, as shown in the diagrams that follow:
- Recommended deployment: Uses two virtual services to load balance the Meditech API servers which then make a connection to the Cache servers and any other Meditech related server, such as Platform Service, File Library, Monitor Service on the backend.
- Minimum deployment: Uses two virtual services to load balance the Meditech API servers which have both the API and Cache services installed on the same server. The server then makes a connection to the other Meditech related servers, such as Platform Service, File Library, Monitor Service on the backend.
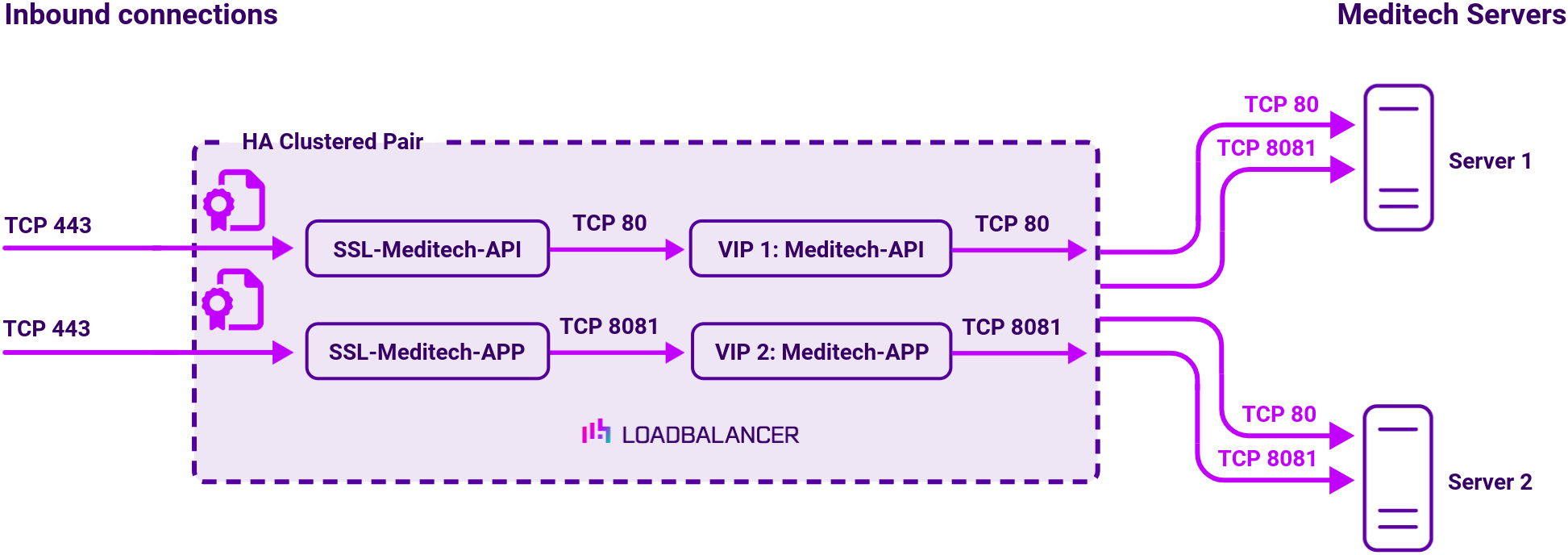
Scenario 1: Recommended deployment using SSL offloading
Here, the connection to the appliance is encrypted, but the connection from the appliance to the RESTful services is not.
| Ref. | VIP Name | Mode | Port(s) | Persistence Mode | Health Check |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIP 1 | Meditech-API | Layer 7 Reverse Proxy | 80 | None | HTTP (HEAD) |
| VIP 2 | Meditech-APP | Layer 7 Reverse Proxy | 8081 | None | HTTP (HEAD) |
In this deployment, two virtual services are used in addition to a TLS/SSL termination. The virtual services use Layer 7 Reverse Proxy. An SSL certificate is uploaded and associated to the Virtual Service. Data is encrypted from the client to the load balancer, but is unencrypted from the load balancer to the backend servers as shown below:
Note
The load balancer can be deployed as a single unit, although Loadbalancer.org recommends a clustered pair for resilience and high availability.
SSL Termination is configured on the load balancer for both VIP1 and VIP2. This provides a corresponding HTTPS Virtual Service for these VIPs. Certificates in PEM or PFX format can be uploaded to the load balancer.
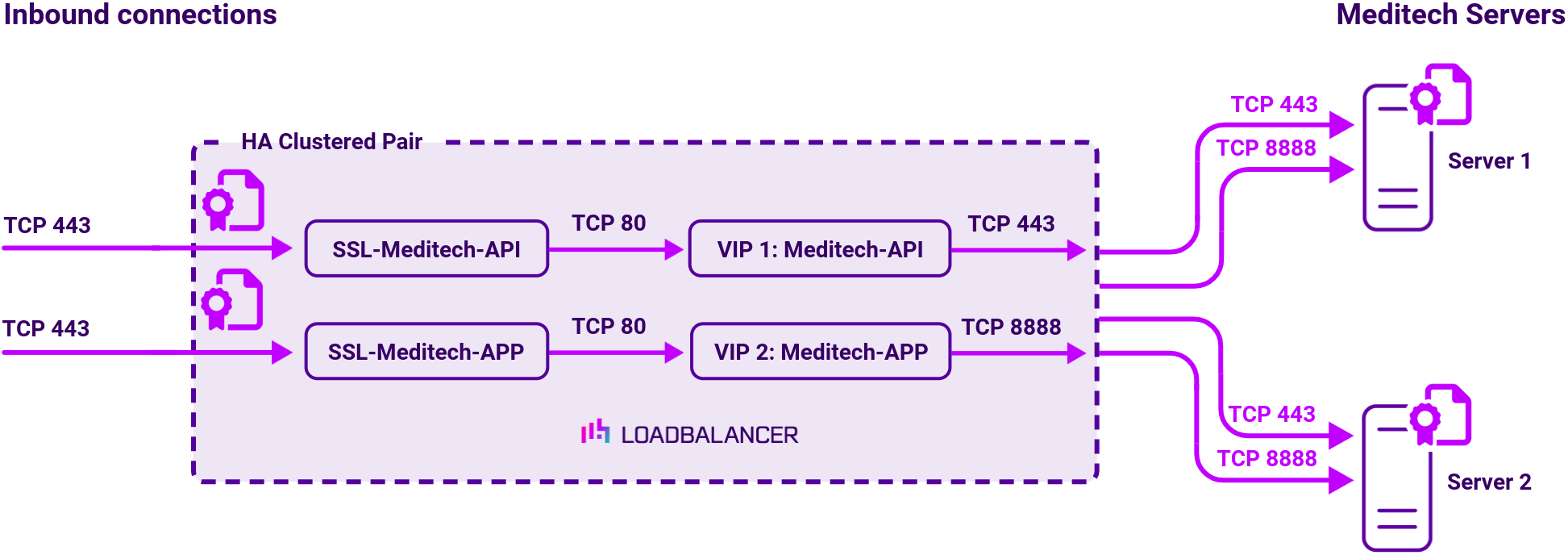
Scenario 2: Recommended deployment using SSL bridging
Here, the connection to the appliance is encrypted and the connection from the appliance to the API servers is also encrypted.
| Ref. | VIP Name | Mode | Port(s) | Persistence Mode | Health Checks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2 – VIP 1 | Meditech-API | Layer 7 Reverse Proxy | 80 | None | HTTPS (HEAD) |
| S2 – VIP 2 | Meditech-APP | Layer 7 Reverse Proxy | 8888 | None | HTTPS (HEAD) |
In this deployment, two virtual services are used in addition to a TLS/SSL termination. The virtual services use Layer 7 Reverse Proxy with re-encrypt to backend enabled. An SSL certificate is uploaded and associated to the Virtual Service. Data is encrypted from the client to the load balancer and is also encrypted from the load balancer to the backend servers as shown below:
Note
The load balancer can be deployed as a single unit, although Loadbalancer.org recommends a clustered pair for resilience and high availability.
As per option 1, SSL Termination is configured on the load balancer for VIP1 and VIP2. In addition, backend re-encryption is also enabled for both VIPs. This forces the connections from the appliance to the backend (Real) servers to be encrypted.