Load balancing Fiserv DNAconnect
Benefits of load balancing Fiserv DNAconnect
Load balancing the Fiserv DNAconnect interface results in High Availability, scalability and enhanced performance:
- High Availability (HA): Load balancing eliminates the single point of failure by distributing incoming client requests across multiple DNAconnect servers. If one DNAconnect server fails, the load balancer automatically detects the failure (via health checks) and redirects all traffic to the remaining healthy servers. This seamless failover ensures that the critical system interfaces remain accessible and operational, maximizing uptime and providing a more reliable service for the financial institution’s internal and external users.
- Scalability for future growth: Load balancing provides the flexibility to adjust the infrastructure dynamically as the financial institution’s transaction volume and business needs change. If transaction volumes increase due to new products, services, or business growth, additional DNAconnect servers can be seamlessly added to the server pool behind the load balancer to handle the increased load. Servers can be taken offline for maintenance, upgrades, or patches without impacting service availability, as the load balancer simply routes traffic away from the server being serviced.
- Enhanced performance: By distributing the workload, a load balancer prevents any single server from becoming overwhelmed, which is crucial during peak transaction periods. It uses various algorithms (like Round Robin or Least Connections) to ensure the request load is spread efficiently among all available DNAconnect servers. This even distribution prevents resource exhaustion on any one server, leading to faster response times and lower network latency for applications and services communicating with the core DNA system.
About Fiserv DNAconnect
DNAconnect is a suite of applications and services that facilitate the creation and processing of interfaces between different systems you can use to support communication between a source system and one or more target systems.
Why Loadbalancer.org for Fiserv DNAconnect?
Loadbalancer’s intuitive Enterprise Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is also designed to save time and money with a clever, not complex, WebUI.
Easily configure, deploy, manage, and maintain our Enterprise load balancer, reducing complexity and the risk of human error. For a difference you can see in just minutes.
And with WAF and GSLB included straight out-of-the-box, there’s no hidden costs, so the prices you see on our website are fully transparent.
More on what’s possible with Loadbalancer.org.
How to load balance Fiserv DNAconnect
The load balancer can be deployed in 4 fundamental ways: Layer 4 DR mode, Layer 4 NAT mode, Layer 4 SNAT mode, and Layer 7 Reverse Proxy (Layer 7 SNAT mode).
For Fiserv DNAconnect, Layer 4 DR mode is the recommended deployment method.
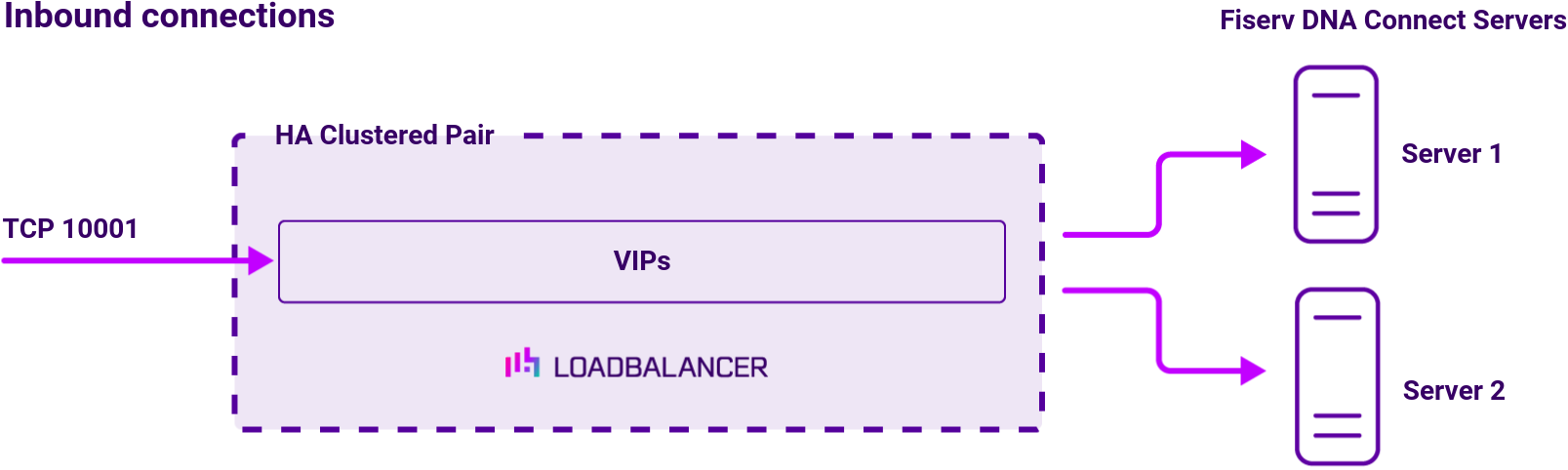
Port requirements
The following table shows the ports that are load balanced:
| Port(s) | Protocol | Use |
|---|---|---|
| 80 | TCP | HTTP – Fiserv |
| 2500, 2501, 2507,2601, 2655, 2656,2999 | TCP | DNAconnect – Fiserv |
Load balancing deployment concept
About Layer 4 DR mode load balancing
One-arm direct routing (DR) mode is a very high performance solution that requires little change to your existing infrastructure.
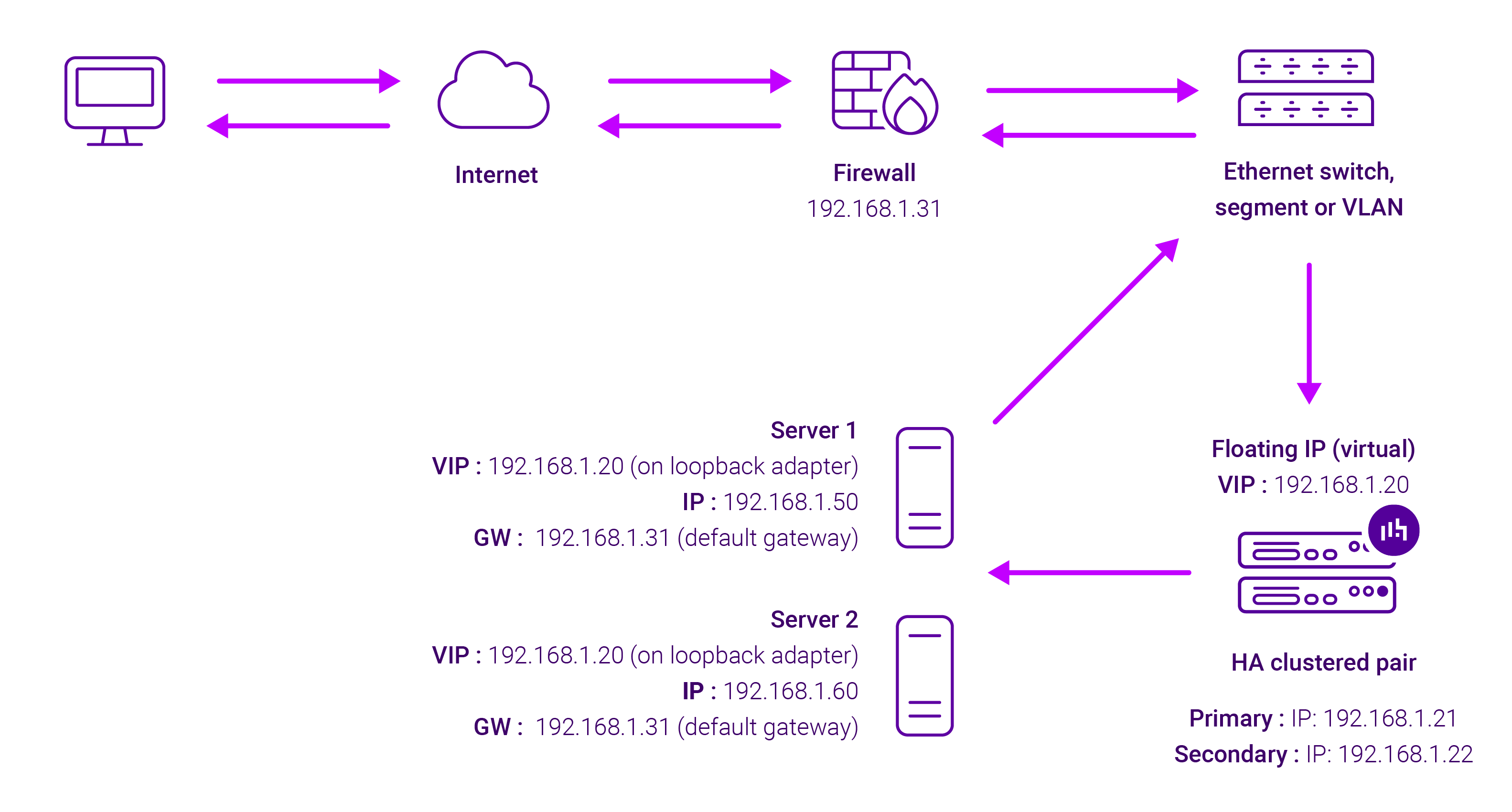
DR mode works by changing the destination MAC address of the incoming packet to match the selected Real Server on the fly which is very fast.
When the packet reaches the Real Server it expects the Real Server to own the Virtual Services IP address (VIP). This means that you need to ensure that the Real Server (and the load balanced application) respond to both the Real Server’s own IP address and the VIP.
The Real Servers should not respond to ARP requests for the VIP. Only the load balancer should do this. Configuring the Real Servers in this way is referred to as Solving the ARP problem.
On average, DR mode is 8 times quicker than NAT for HTTP, 50 times quicker for Terminal Services and much, much faster for streaming media or FTP.
The load balancer must have an Interface in the same subnet as the Real Servers to ensure Layer 2 connectivity required for DR mode to work.
The VIP can be brought up on the same subnet as the Real Servers, or on a different subnet provided that the load balancer has an interface in that subnet.
Port translation is not possible with DR mode, e.g. VIP:80 → RIP:8080 is not supported. DR mode is transparent, i.e. the Real Server will see the source IP address of the client.