Benefits of load balancing Apache HTTP Server
Load balancing Apache HTTP Server provides a number of benefits:
- Performance optimization through SSL/TLS Offloading: Load balancers can handle the computationally intensive process of SSL/TLS encryption and decryption (known as SSL termination). This offloads the workload from your backend web servers. By not having to perform the complex cryptographic operations, the web servers’ CPU and memory resources are freed up to focus entirely on serving the application logic and content. This allows each server to handle more client requests, improving the overall system capacity and responsiveness. Offloading this work to a device specifically designed for it (the load balancer) can speed up the SSL/TLS handshake process, reducing the time clients wait for a secure connection to be established.
- Enhanced scalability: Load balancers enable horizontal scaling, allowing you to add or remove backend servers easily and dynamically to handle fluctuations in traffic, all while the single public-facing HTTPS endpoint remains the same (the load balancer’s IP).
- High Availability (HA): By performing continuous health checks on the backend servers, the load balancer ensures that if any server fails, all HTTPS traffic is instantly and automatically redirected to the remaining healthy servers. This prevents a single server failure from taking your entire service offline.
About Apache
Apache is a commonly used web server, it is used to serve up web pages and applications from many platforms and environments. It is frequently installed to host or serve up pages from applications like content management system or blog engines, written in PHP/Python or other languages.
Apache is a development of the NCSA httpd web server which has been in active development since 1995, it is a key part of the Open Source movement, being free software and part of the LAMP software stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, Perl/PHP/Python). Most Apache instances in deployment are actually Apache version 2 but are still referred to as Apache and makes little/no difference.
Why Loadbalancer.org for Apache HTTP Server?
Loadbalancer’s intuitive Enterprise Application Delivery Controller (ADC) is designed to save time and money with a clever, not complex, WebUI.
Easily configure, deploy, manage, and maintain our Enterprise load balancer, reducing complexity and the risk of human error. For a difference you can see in just minutes.
And with WAF and GSLB included straight out-of-the-box, there’s no hidden costs, so the prices you see on our website are fully transparent.
More on what’s possible with Loadbalancer.org.
How to load balance Apache HTTP Server
Loadbalancer.org supports Apache with all common load balancing methods, incorporating numerous modifications and customisations to suit your requirements and can be deployed physically, virtually or in the cloud.
Protocols and load balancing methods for Apache HTTP Server
| Protocol | Port | Load balancing methods |
|---|---|---|
| HTTP | 80 | Layer 7 SNAT (Recommended) Using Reverse Proxy mode is the easiest and most flexible load balancing method, offering advanced URL switching, cookie insertion and WAF capabilities. Layer 4 DR Direct Routing has the advantage of being fully transparent and seriously fast but requires solving the arp problem. Layer 4 NAT Traditional NAT mode gives easy to implement fast and transparent load balancing but usually requires a two-arm configuration (two subnets). |
| HTTPS | 443 | All load balancing methods can be easily configured for SSL Pass-through. This has the advantage of being fast, secure and easy to maintain. Identical SSL certificates will need to exist on each of your backend servers for pass-through security. SSL Termination or off-loading must be used when advanced Layer 7 functionality such as cookies or URL switching is required. You can also implement SNI if you have multiple domain certificates one public IP address. Optional re-encryption is also available between the load balancer and Apache. |
| HTTP/2 | N/A | Layer 7, support is imminent, this is due/expected in the 8.3.4 timeframe. |
| Proxy Protocol | N/A | Apache support from v.2.4.31 |
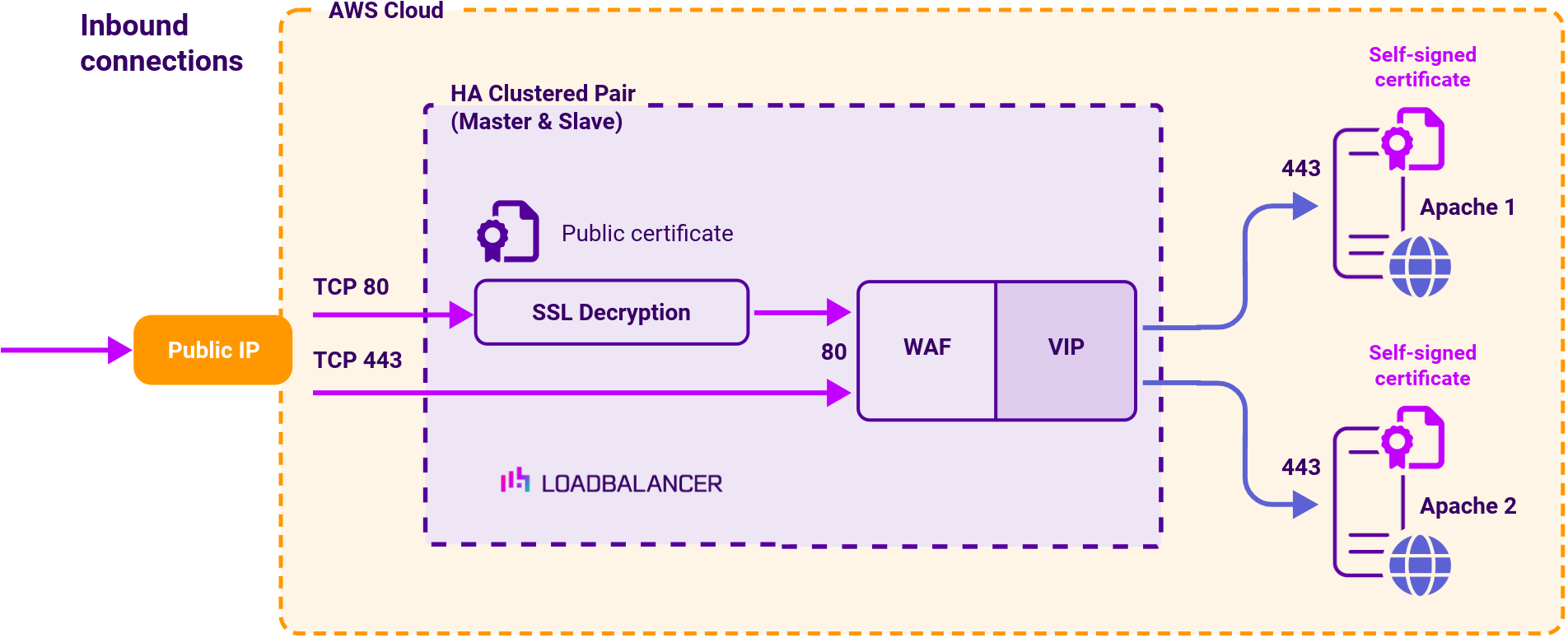
Load balancing deployment concept
AWS cloud
Azure cloud